Pulmonary Embolism
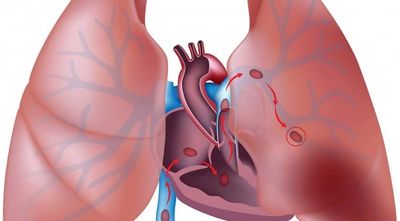
A pulmonary embolism (PE) happens when one of the arteries in the lungs gets blocked by a blood clot. In most cases, the clot travels from the leg or another part of the body (called deep vein thrombosis) and blocks the flow of blood to the lung, making it life-threatening. It can also lead to pulmonary hypertension.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a pulmonary embolism vary greatly depending on the size of the clot, how much of the lung is involved, and whether you have an underlying medical condition. The most common symptoms are:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain that becomes worse when taking a breath
- Cough which may contain blood
- Leg pain or swelling
- Pain in you back
- Excessive sweating
- Lightheaded, dizziness or passing out
- Blueish lips or nails
Diagnosis
Common tests to diagnosis PE include:
- Computed tomographic angiography
- D-Dimer blood tests
- Chest x-ray
- Pulmonary V/Q scan
- Leg ultrasound
- Spiral CT scan
- Pulmonary angiography
- Electrocardiogram
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at keeping the blood clot from getting bigger and preventing new clots from forming. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent serious complications or death.
The most common treatment for a blood clot in the lung is blood thinners or anticoagulants. Patients will normally have to take medications regularly for an indefinite amount of time, usually at least 3 months.
Surgical or catheter extraction can also be performed for a very large, life-threatening clot. A flexible tube (catheter) is threaded through the blood vessels to remove the clot.
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.